A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Management in the Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry is a high-stakes environment. A single incident of foodborne illness or a product recall can have devastating consequences for a company's reputation, finances, and even its survival. Therefore, a robust and comprehensive risk management strategy is absolutely crucial. This article provides a deep dive into the key aspects of effective risk management within the F&B sector.
Understanding the Landscape of Risks
Before implementing any risk management strategy, it's essential to identify and categorize the potential hazards. These risks can be broadly classified into several categories:
-
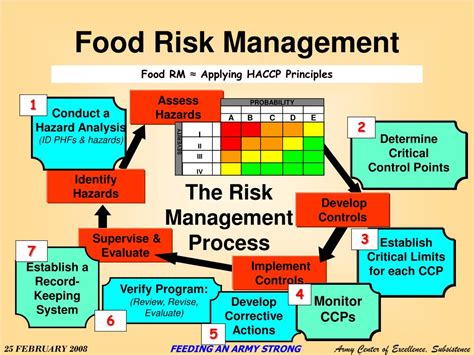
Food Safety Hazards: This is arguably the most critical area. Risks include contamination from biological (bacteria, viruses, parasites), chemical (pesticides, cleaning agents), and physical (glass, metal) sources. HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a widely adopted system for identifying and controlling these hazards throughout the entire food production chain.
-
Supply Chain Risks: Disruptions to the supply chain, due to natural disasters, political instability, or supplier failures, can significantly impact production and profitability. Diversifying suppliers and building strong relationships are crucial mitigation strategies.
-
Operational Risks: These encompass a wide range of issues, including equipment malfunctions, power outages, employee errors, and inadequate training. Regular equipment maintenance, robust employee training programs, and emergency preparedness plans are vital.
-
Reputational Risks: Negative publicity, social media controversies, and product recalls can severely damage a company's brand image and consumer trust. Proactive crisis communication strategies and robust quality control measures are essential for managing reputational risk.
-
Regulatory Compliance Risks: The food and beverage industry is heavily regulated. Failure to comply with food safety regulations, labeling requirements, and other legal obligations can lead to hefty fines and legal action. Staying updated on current regulations and maintaining meticulous records are crucial.
Implementing an Effective Risk Management System
A well-structured risk management system should follow these key steps:
1. Risk Identification and Assessment: This involves systematically identifying all potential hazards and evaluating their likelihood and potential impact. Techniques like brainstorming, SWOT analysis, and FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) can be employed.
2. Risk Prioritization: Once risks are identified and assessed, they should be prioritized based on their severity and likelihood. This allows resources to be allocated effectively to address the most critical threats first.
3. Risk Mitigation Strategies: This involves developing and implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate the identified risks. These strategies can include preventative measures, such as improved sanitation practices, employee training, and equipment maintenance, as well as contingency plans for dealing with unforeseen events.
4. Monitoring and Review: The risk management system should be regularly monitored and reviewed to ensure its effectiveness. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting regular audits, and updating the system as needed to reflect changes in the business environment or regulatory landscape. Regular internal audits and external audits are critical.
5. Continuous Improvement: The process should be cyclical, with lessons learned from past incidents and near misses being used to improve the system over time. A culture of safety and continuous improvement is vital for success.
Key Technologies in Risk Management
Modern technology plays a crucial role in effective risk management:
-
Traceability Systems: These allow companies to track food products throughout the entire supply chain, facilitating rapid identification and removal of contaminated products in case of a recall.
-
Data Analytics: Analyzing data from various sources can help identify trends, predict potential problems, and improve decision-making.
-
Automation: Automation of tasks can reduce human error and improve consistency in processes.
By implementing a robust risk management system, food and beverage companies can significantly reduce their exposure to hazards, protect their reputation, and ensure the safety and quality of their products. Remember, proactive risk management is not just a cost; it's a critical investment in the long-term success and sustainability of your business.